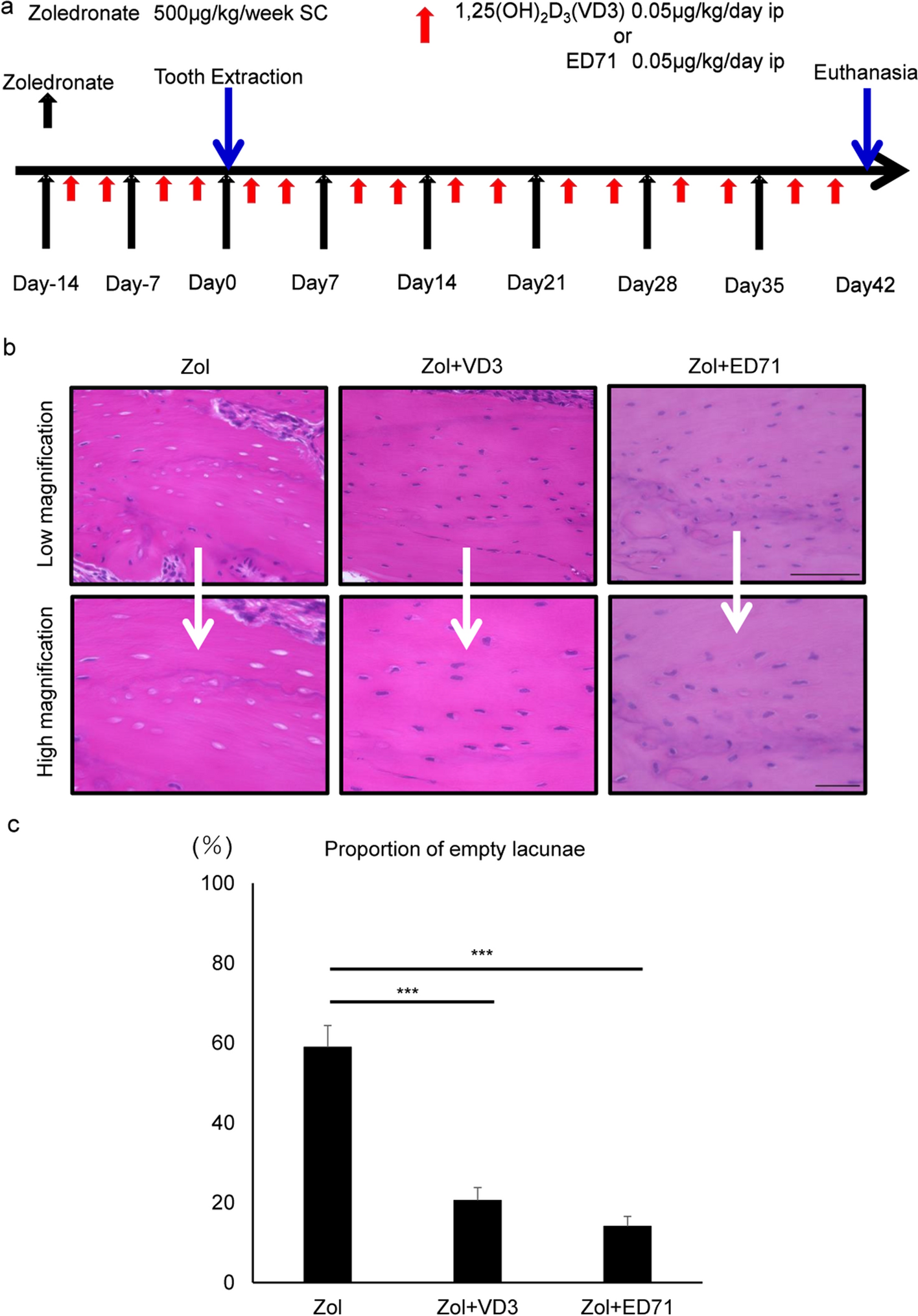
Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics

Cells, Free Full-Text
Biomolecules, Free Full-Text

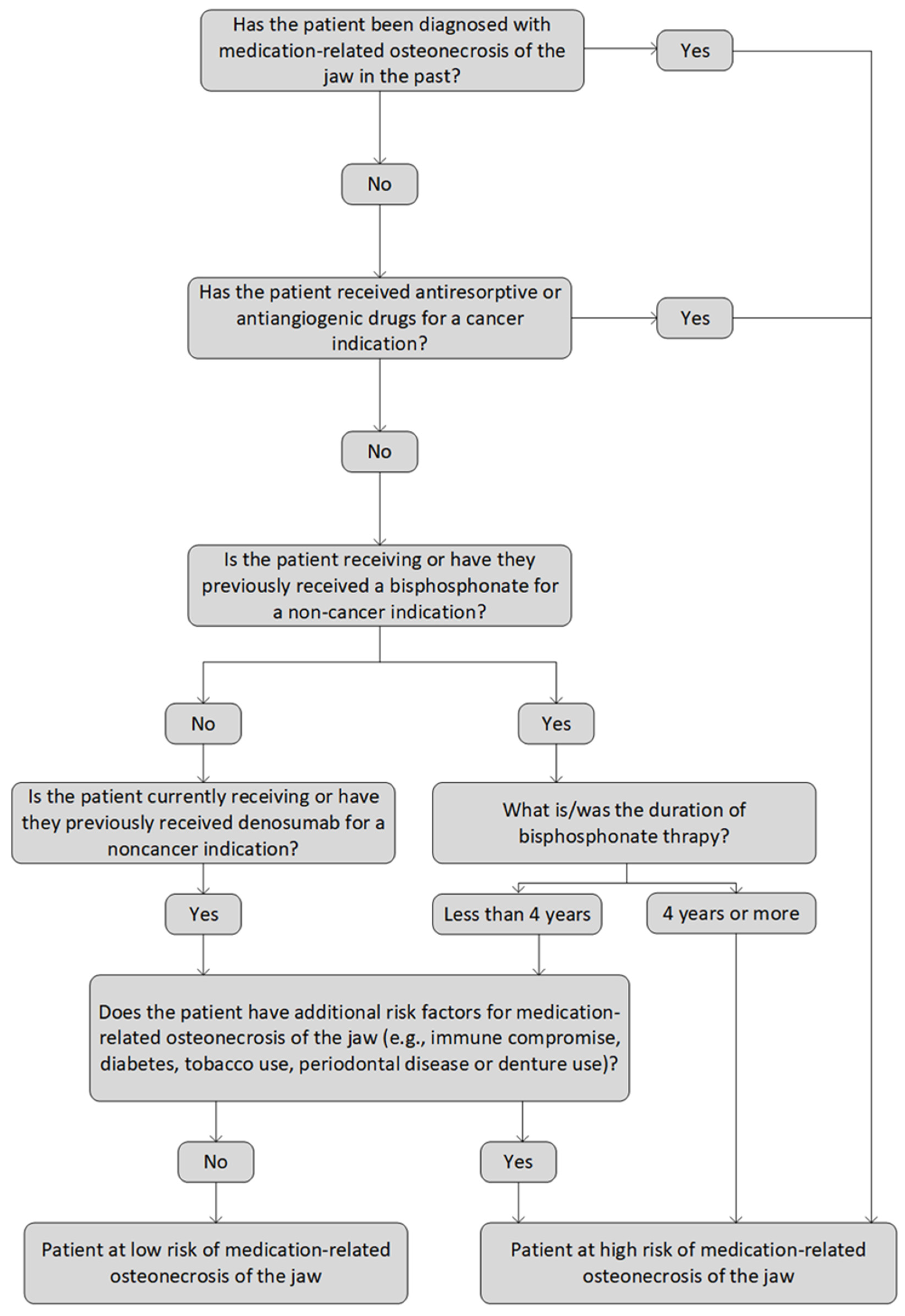
Pathophysiology of Medication‐Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—A Minireview - Tetradis - 2023 - JBMR Plus - Wiley Online Library

Pathophysiology of Medication‐Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—A Minireview - Tetradis - 2023 - JBMR Plus - Wiley Online Library

Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws after tooth extraction in senescent female mice treated with zoledronic acid: microtomographic, histological and immunohistochemical characterization

Experimental schedule. Zoledronic acid (Zol) at 3 different doses is

Elevation of pro-inflammatory cytokine levels following anti-resorptive drug treatment is required for osteonecrosis development in infectious osteomyelitis

Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics

IJMS, Free Full-Text
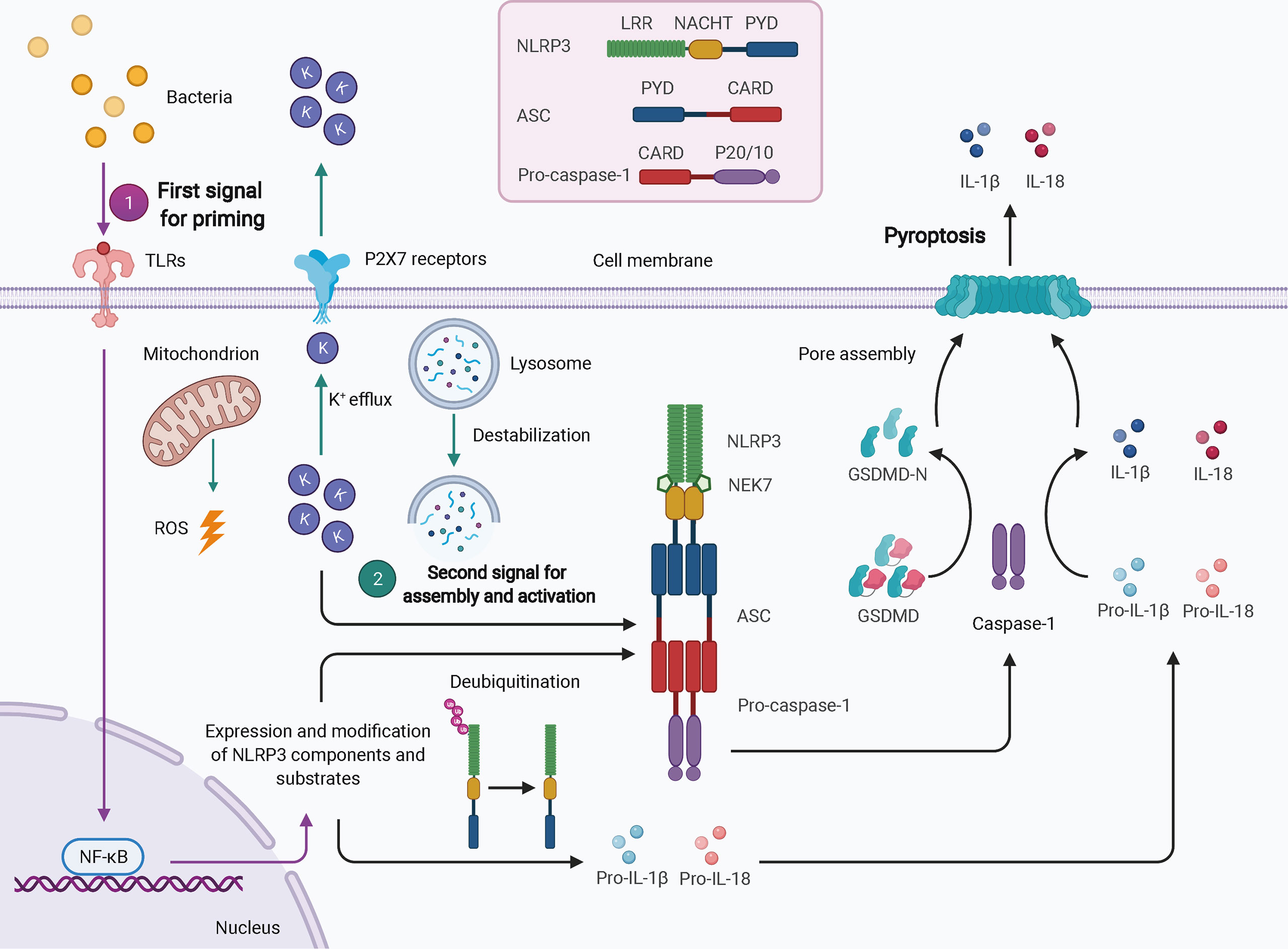
Frontiers Inflammasomes in Alveolar Bone Loss

PDF) Osteonecrosis development by tooth extraction in zoledronate treated mice is inhibited by active vitamin D analogues, anti-inflammatory agents or antibiotics

Indigenous microbiota protects development of medication-related osteonecrosis induced by periapical disease in mice

Infection and Medication-related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw - H. Katsarelis, N.P. Shah, D.K. Dhariwal, M. Pazianas, 2015

Pathophysiology of Medication‐Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—A Minireview - Tetradis - 2023 - JBMR Plus - Wiley Online Library